BLOG
Chronological vs. Biological Aging: Differences & More

What Is Chronological Age?
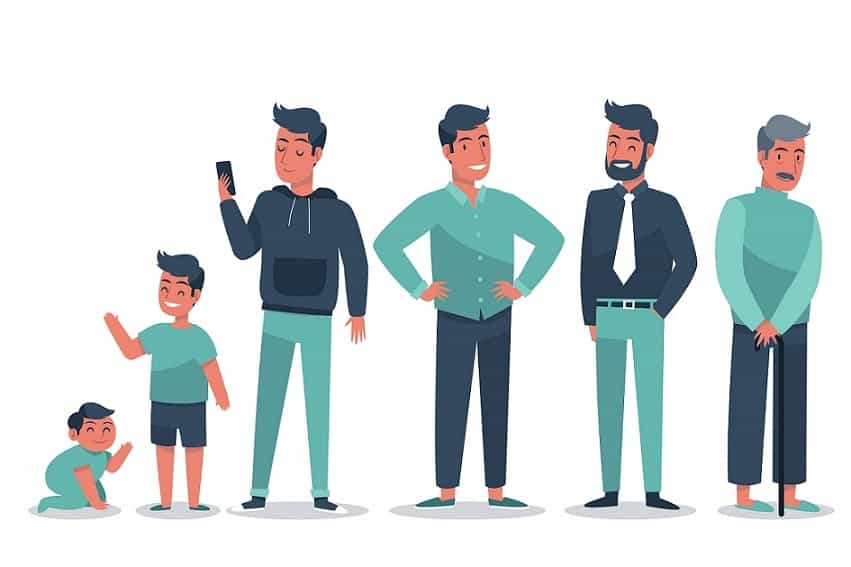
The number of years that an individual has been living from birth to the given date is known as the chronological age. In simple wording, we say that it is the measure of age which is based on the passage of time from the birth of a person. This process is unchangeable which means the certain amount of time that you have spent can never be changed.
However, you’re surprised to look at some people whose chronological age is different from the original and they seem much older or younger. If you want to make positive changes in your body, then you need to have control over aging because this provides an incentive to develop a healthier lifestyle
What Is Biological Age?
The process which is refers to how old a human’s body is looking. The biological age is also known as the physiological age which is based on many factors including health markers, functions, and genetic factors. Rather than counting the years, biological age is assessed through evaluations and medical tests.
Experts have an overview that the DNA is a state that has a reflection on biological aging therefore, this aging process helps to analyze how soon you’ll die. The chronological age is significantly different from the biological age and this seems a complex task to evaluate therefore, we use the biological age calculator which is developed to determine the biological age to the chronological age and reveal the age that the body is truly at.
Factors Affecting The Aging Process:
In summary, the possibility is that genetic aging has a crucial role, as lifestyle preferences appear to be more significant to physical aging. In this context, the biological age calculator provides valuable insights that influence the aging process.
By utilizing the below-given factors the tool helps to understand how health habits have an impact on the aging rate. These factors include:
- Genetics: It influences the turnover of cells, the repairing ability of cells, and collagen production.
- Lifestyle: The factors of lifestyle including exercise, diet, and management of stress have an impact on the aging process.
- Environmental factors: These factors can accelerate aging including pollution, toxins, and UV radiation.
- Hormones: The balancing of hormones plays a key role so we say imbalances of hormones during andropause/menopause can impact aging.
- Chronic Diseases: These diseases including heart problems, diabetes, and cancer can damage cells and tissues.
- Mental Health: The aging process also be influenced by stress, anxiety, and depression.
Common Differences Between Chronological & Biological Age:
External Factors:
Many external factors have influenced both the aging terms. In chronological aging, without considering individual differences it takes into service the passage of time while physiological aging is influenced by health habits and lifestyle factors.
Physical Appearance:
As we have discussed above you are surprised to see that some people are looking younger or older than your original age. Biological age is influenced by physical appearance based on muscle tone, skin elasticity, and overall vitality.
Health & Functionality:
Both aging processes offer insight view of overall health and functioning capabilities. People in their 50s might exhibit biological age that mirrors a healthier lifestyle and better physiological functions, which helps to align their health on par with individuals in their 40s chronologically.
Cellular Aging:
The cells and the tissues are influenced by the body's health and have an impact on biological aging. Telomere is a marker of cellular aging and this cell is associated with aging acceleration. Cellular aging can arise from ongoing cellular damage or the unfolding of predetermined genetic material in the cell.
Genetic Factors:
For identical twins, chronological age is considered the same while the biological ages differ based on lifestyle choices and predisposition genetics. These factors including DNA, hormonal balancing, general health condition, and cognitive functioning influence how the body ages and responds to the stressors of the environment.
Disease & Medical Conditions:
The biological age of an individual can provide health issues that can highlight the health conditions and are not immediately observable. Suppose someone in the 40s age has a biological age and shows poor health conditions due to diabetes, arthritis, and heart diseases.
Key Takeaways:
Research has indicated that the biological age is a more prominent term than the chronological age for predicting the onset of disease and death. Overall there are many factors including lifestyle, environmental factors, hormonal balancing, genetics, and psychological terms play a significant role in shaping how we age, and by this way, we can determine how many years we are alive. By addressing the above discussed we can promote healthy aging which leads to potentially slowing down the aging process.